The iShares Ethereum Trust ETF and iShares Bitcoin Trust ETF are not investment companies registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940, and therefore are not subject to the same regulatory requirements as mutual funds or ETFs registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940.
Bitcoin vs. Ethereum: Similarities, differences and considerations
Jul 22, 2024 COMMODITY
Why it’s important for investors to understand how the two leading digital assets are different.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- As the digital assets space evolves, it’s important for investors to understand the distinctions between the two largest cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin and Ether.
- Bitcoin’s strength lies in its simplicity, scarcity and credibility as an alternative monetary instrument that exists independently from governments and central banks.
- Ethereum’s appeal is in its flexibility and ability to support decentralized applications through smart contracts. This makes it analogous to a revenue-generating app store that’s open source.
- Given these fundamental differences, investors can view Bitcoin and Ethereum not as competitors but as distinct assets. They each address different use cases and reflect different drivers of return and risk.
INTRODUCTION OF BITCOIN AND ETHEREUM
Bitcoin and Ether are the two largest cryptocurrencies by market capitalization and play pivotal roles in the broader blockchain ecosystem.1 Both assets have attracted significant attention from investors, developers, and enterprises due to their unique features and potential applications.
But how could investors consider these assets for their portfolios? This comparison aims to help potential investors understand the nuances between Bitcoin and Ethereum, focusing on their underlying technology, value propositions, and investment theses.
Figure 1: Bitcoin and Ether have emerged as the world’s predominant cryptoassets
Share of total cryptoasset market cap
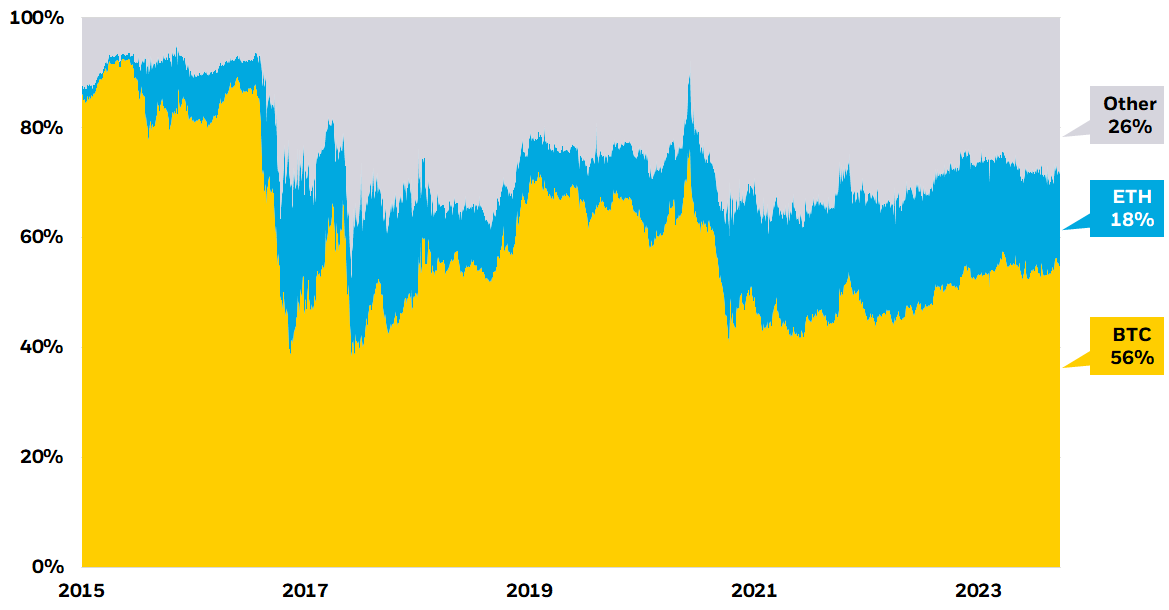
Source: The Tie and CoinGecko, as of April 30, 2024. Ethereum’s market capitalization is measured by its native token, ether. BNB is the third largest non-stablecoin cryptoasset and it comprises less than 4% of the crypto market.
Chart description: Stacked area chart displaying the total cryptoasset market cap held by Bitcoin, Ethereum and other cryptoassets.
WHAT ARE THE MAIN DIFFERENCES BETWEEN BITCOIN AND ETHEREUM?
Bitcoin
Bitcoin, launched in 2009, was the first was the first digital asset to gain widespread global adoption and it remains the largest by market cap today. Bitcoin is designed to serve as a decentralized alternative to traditional government-issued money, and it enables value to be transferred between peers without a centralized intermediary. (Read more about Bitcoin)
Among its key features:
- Simplicity: Bitcoin focuses on facilitating simple value transfers, with limited ability to be used for other applications, reducing technical risk.
- Fixed supply: New issuance of Bitcoin is halved about every four years, with total Bitcoin supply capped at 21 million coins.2 (Learn more about the Bitcoin halving)
- Stability: It is difficult to change Bitcoin’s code, reinforcing its value proposition as an alternative monetary instrument rather than a constantly evolving technology platform.
Ethereum
Ethereum, launched in 2015, is a flexible blockchain enabling the next generation of decentralized applications (dApps) to emerge through the introduction of self-executing contracts, known as smart contracts. Think of Ethereum as an open-source app store that generates revenues as more users interact with applications on Ethereum, including tokenized assets, like stablecoins, or decentralized financial services. Ethereum’s native currency, ether, is the token used to transact in the Ethereum ecosystem. Among its key features:
- Flexibility: Ethereum is designed to be flexible and can execute more complex transactions, giving it a variety of use cases.
- Dynamic supply: The supply of ether is dynamic, and ether’s supply can shrink or grow depending on several variables, including network usage.
- Constantly evolving: Ethereum has the largest blockchain developer community focused on building applications and making technical improvements to the protocol to support the next generation of applications.3
Figure 2: Understanding key differentiators between Bitcoin and Ethereum
| BITCOIN | ETHEREUM | |
|---|---|---|
| Value proposition | Internet-native global monetary alternative | Programmable platform enabling the execution of decentralized applications |
| Launch date | January 2009 | July 2015 |
| Founder | Satoshi Nakamoto (pseudonymous) | Vitalik Buterin |
| Market cap (rank) | $1.2T (1st) | $411B (2nd) |
| Supply cap | Fixed; 21 million | Variable; based on staking participation, on-chain activity, and transaction fees |
| Consensus mechanism | Proof of work | Proof of stake |
Source: CoinGecko as of July 2, 2024. The above table is for illustration purposes only. It serves as a general summary and is not exhaustive. This information should not be relied upon as a primary basis for an investment decision.
HOW DO INVESTORS VIEW BITCOIN AND ETHEREUM?
While Bitcoin and Ethereum share similarities, namely that they are both digital assets untethered from government-issued currencies and central bank policy, their points of distinction are notable for how investors may view them in a portfolio context.
- Bitcoin’s value proposition lies in its role as a finite supply, non-sovereign monetary alternative. It is largely seen as an instrument to hold wealth and potentially hedge against inflation and economic instability. Bitcoin’s simplicity and lack of ties to the real economy make it a pure expression of decentralization, providing potential insulation from the challenges associated with any one nation or government. (Learn more about investing in Bitcoin)
- Ethereum’s value proposition lies in its flexibility and ability to support more sophisticated applications beyond simple value transfers, including supporting DeFi (decentralized financial services), stablecoins (tokenized fiat currencies), and tokenized securities, to name a few. An investment in Ethereum is a belief that more applications will be built on its open and permissionless programming infrastructure, attracting more users, more revenue, and expanding the universe in which ether resides as a programmable form of money.
Figure 3: Understanding prominent investment themes
| GLOBAL MONETARY ALTERNATIVE | BET ON BLOCKCHAIN ADOPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Global, decentralized, and non-sovereign asset that could serve as a hedge against increasing global disorder and declining trust in governments, banks, and fiat currencies | Core infrastructure that underpins a diverse range of blockchain-based applications and is crucial to the continued adoption and integration of blockchain technology | ||
| Prevalent narrative | BITCOIN | ETHEREUM |
CONCLUSION
As the cryptocurrency market matures, understanding the nuances of each asset will be crucial for informed investment decisions.
Bitcoin and Ethereum offer distinct value propositions for investors. Bitcoin’s strength lies in its simplicity, immutability, and status as the most credible non-sovereign monetary alternative. In contrast, Ethereum's appeal is its versatility and potential to revolutionize various industries with smart contract-powered dApps.
Bitcoin's future is closely tied to its adoption as a non-sovereign alternative to government-issued money, while Ethereum's future will be shaped by its technological advancements and expanding use cases. We believe a blend of these assets may provide a more representative exposure to the quickly evolving crypto market than either of them in isolation. Investors may want to consider their risk tolerance, investment horizon, and the specific attributes of each asset when making investment decisions.

