GLOSSARY:
Bitcoin: Can refer to both the cryptoasset and the blockchain network.
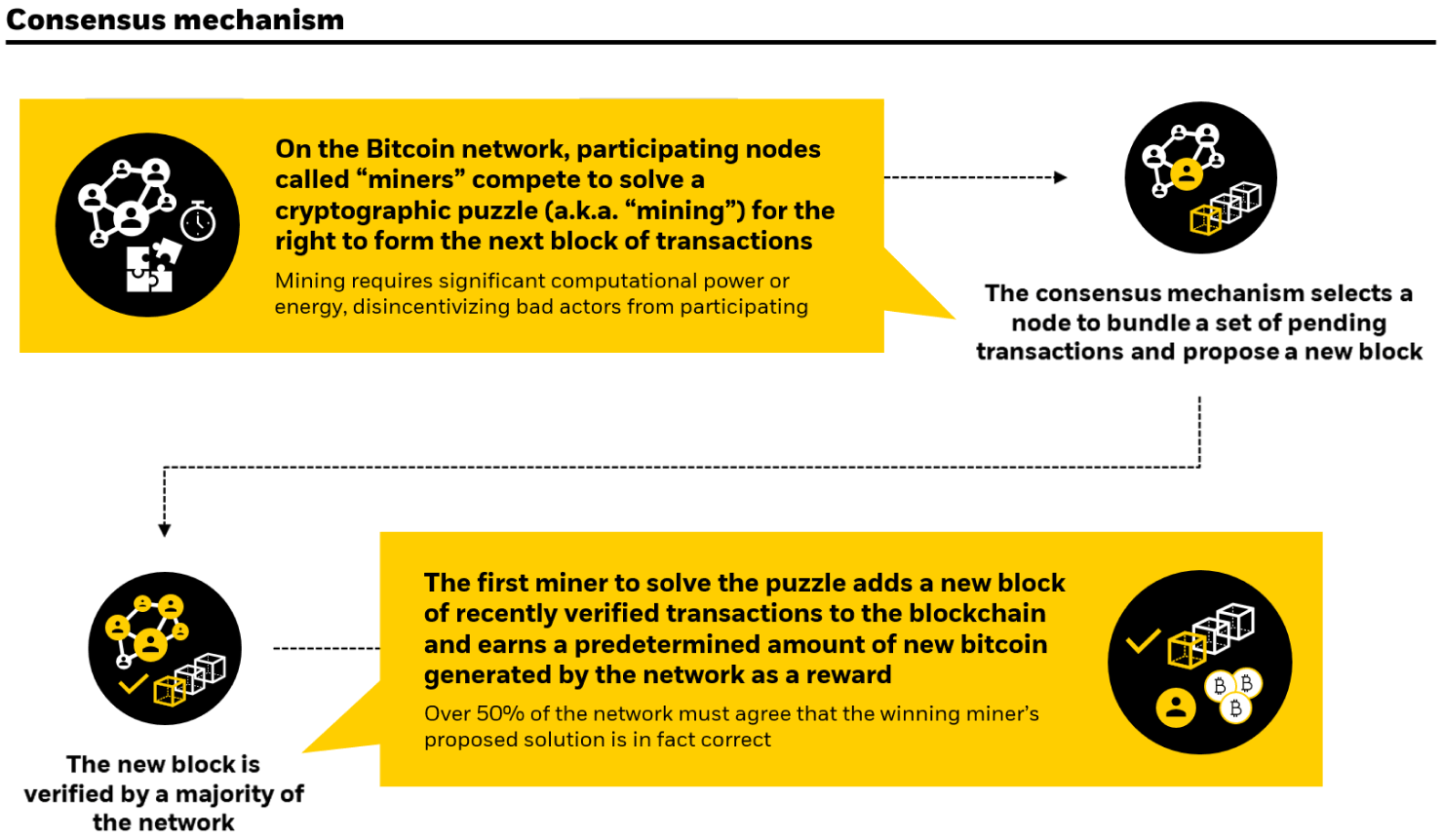
- The protocol, Bitcoin, processes transactions and maintains the ledger via a distributed system of computers running Bitcoin software, known as nodes.
- The asset, bitcoin, is the native token on the Bitcoin network and the world’s leading and most widely adopted cryptoasset2. It is mined, stored, and transferred on a peer-to-peer network via a public ledger, the blockchain.
Blockchain: A distributed digital database that is shared amongst the “nodes” of a network of computers that enables consensus. As a database, a blockchain stores information maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions. The core innovation of blockchain technology is focused on the fidelity and security of a record of data while minimizing trust amongst participants.
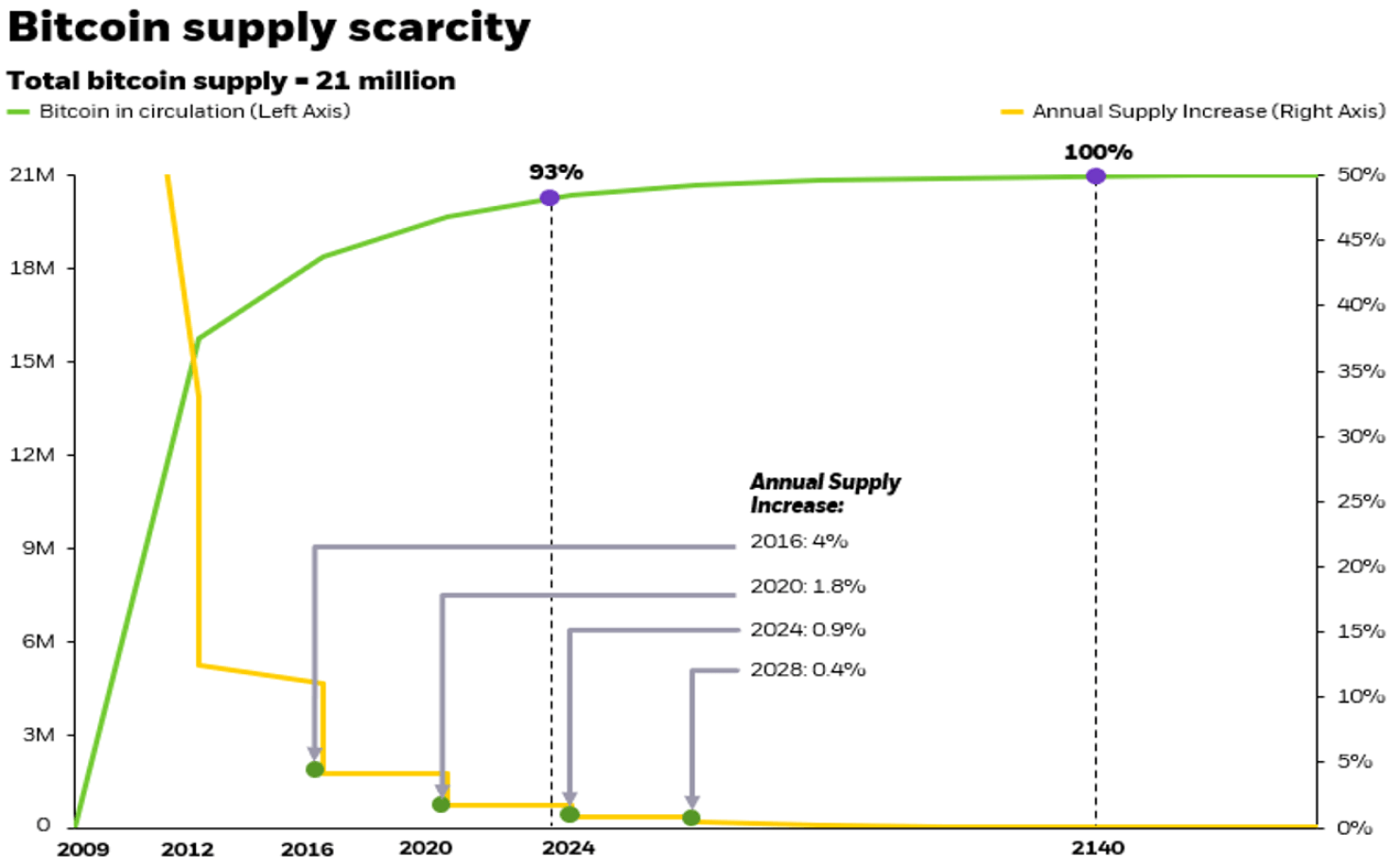
Block rewards: New bitcoin is created with each block and sent to compensate the miner that solved the block. The block reward started at 50 bitcoin when bitcoin was created in 2009. With the most recent halving on April 19, 2024, the rewards declined to 3.125 from 6.25.
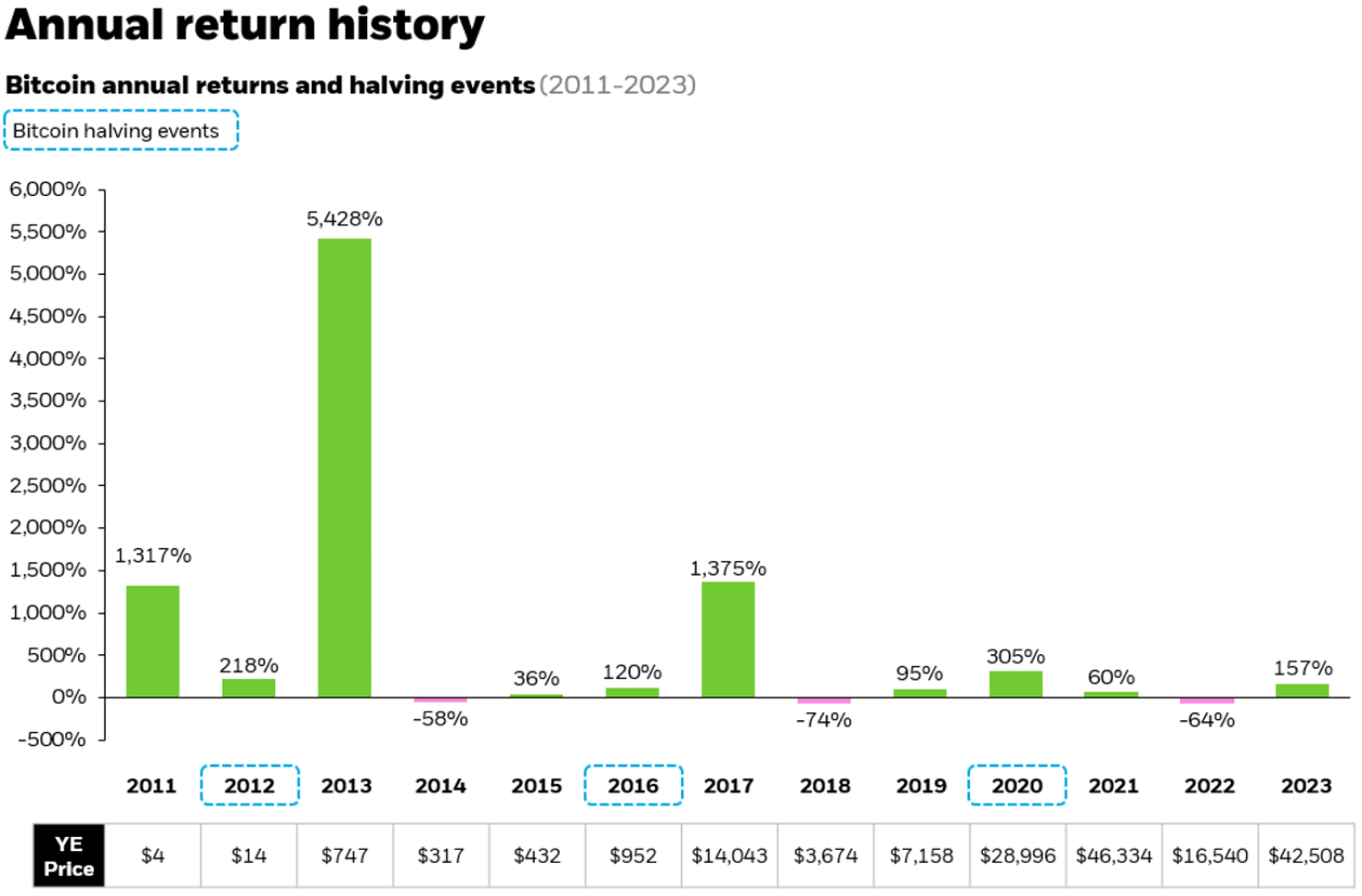
Bitcoin halving: Bitcoin “halving” events occur when the block reward for mining bitcoin transactions is cut in half. These events were written into Bitcoin’s mining algorithm to counteract inflation and maintain fixed supply. In the May 2020 halving, the block reward for a bitcoin “miner” went to 6.25 bitcoin. The next halving in April 2024 reduced the block reward to 3.125 bitcoin. Halvings occur every 210,000 blocks, or approximately every four years.
Hashrate: The combined computational power across all miners securing the Bitcoin network.
1Source: Bloomberg as of April 1, 2024. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
2Source: CoinGecko, as of March 19, 2024. Bitcoin predominance based on its market capitalization of $1.3T, which accounts for greater than 50% of the total market capitalization of all cryptoassets, excluding stablecoins.